Key-locking thread inserts
Custom solutions available upon customer request
Key-locking thread inserts
Custom solutions available upon customer request
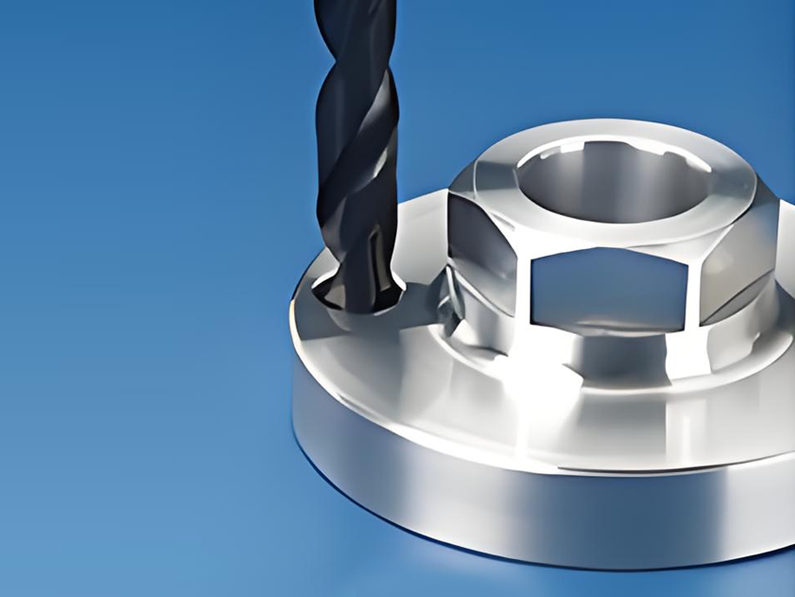
 Product Overview
Product Overview Key-locking thread inserts are special fasteners with both internal and external threads, featuring two or four locking keys on the outer thread. After the insert is installed into the tapped hole, the keys are driven down to lock the insert in place, providing exceptional holding strength.
Today, they are widely used in aerospace, aviation, instrumentation, rail transit, hydraulic and electric equipment, chemical fiber machinery, textiles, and other applications requiring high thread strength.
The fundamental functions of key-locking inserts are thread repair and thread reinforcement. They offer a fast and effective method to restore damaged internal threads, and when used in low-strength materials, significantly enhance the strength of threaded holes.
Classification of Key-Locking Thread Inserts
| ①By Material | ②Surface Treatment | ③By Type / Size Category |
| Carbon steel | Stainless steel SUS303 | Carbon steel — Phosphate anti-corrosion coating Stainless steel 303 — Passivation | Miniature | Thin-wall | Heavy-duty | Extra-strength |
Installation Process of Key-Locking Thread Inserts
1.Drilling:
The drilling depth should be greater than the length of the key-locking insert.

2.Tapping:
The tapped thread specification must match the external thread size of the key-locking insert.
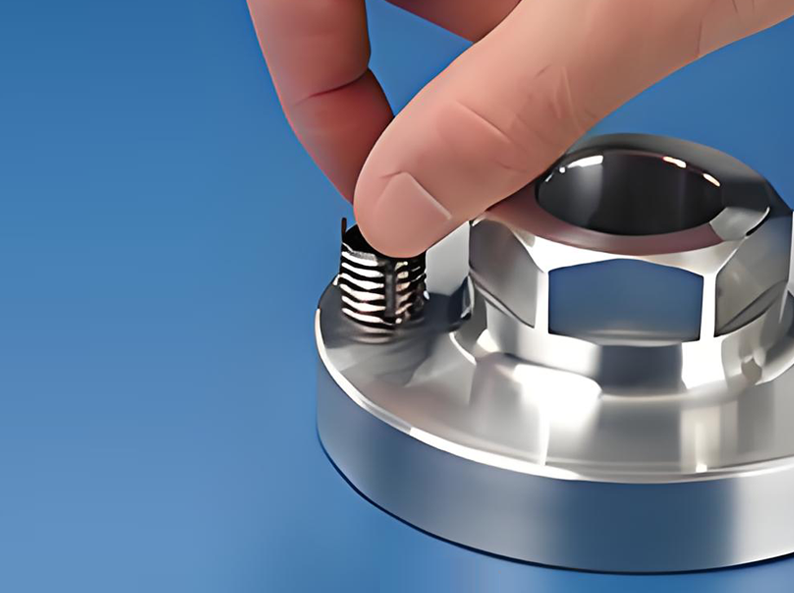

3.Installation:
Screw the key-locking insert into the corresponding threaded hole, ensuring it sits below the workpiece surface.
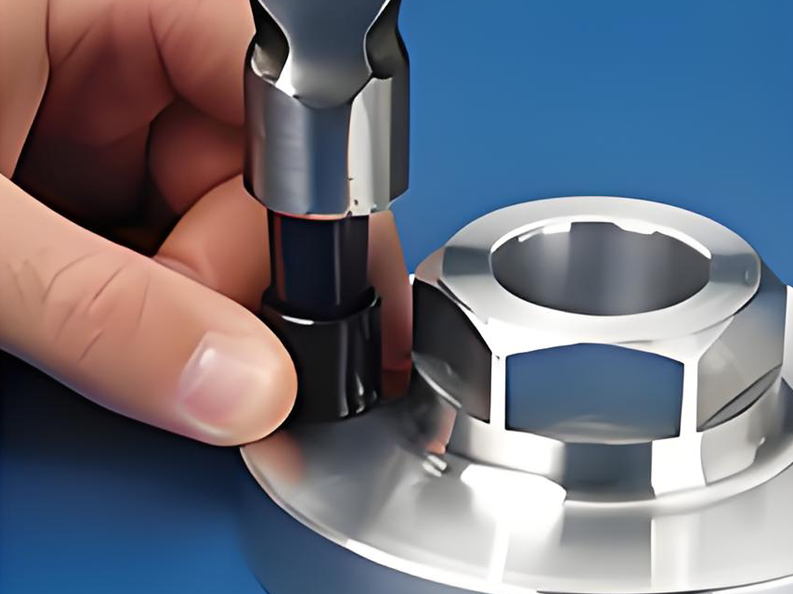

4.Key Locking:
Use the appropriate tool to drive the locking keys of the insert down into the bottom of the hole.
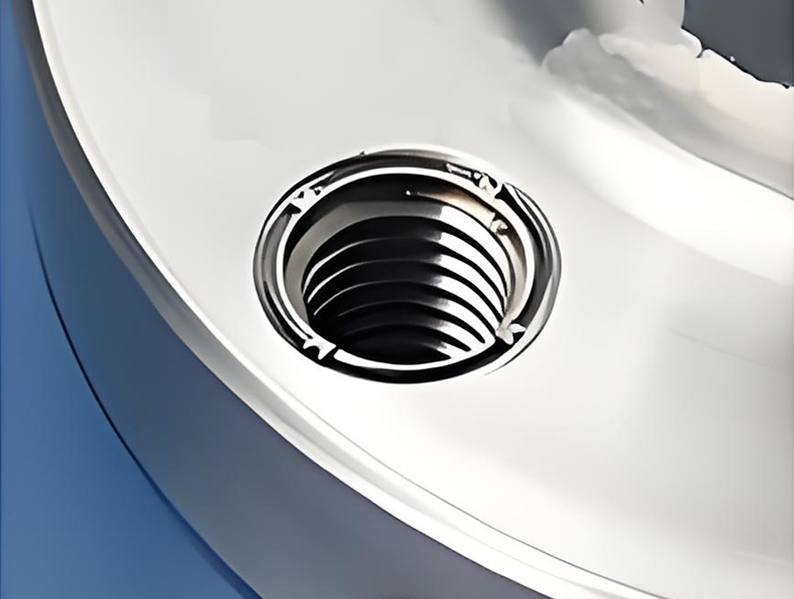

5.Completion:
Illustration of the installation result.
Removal Method for Key-Locking Thread Inserts
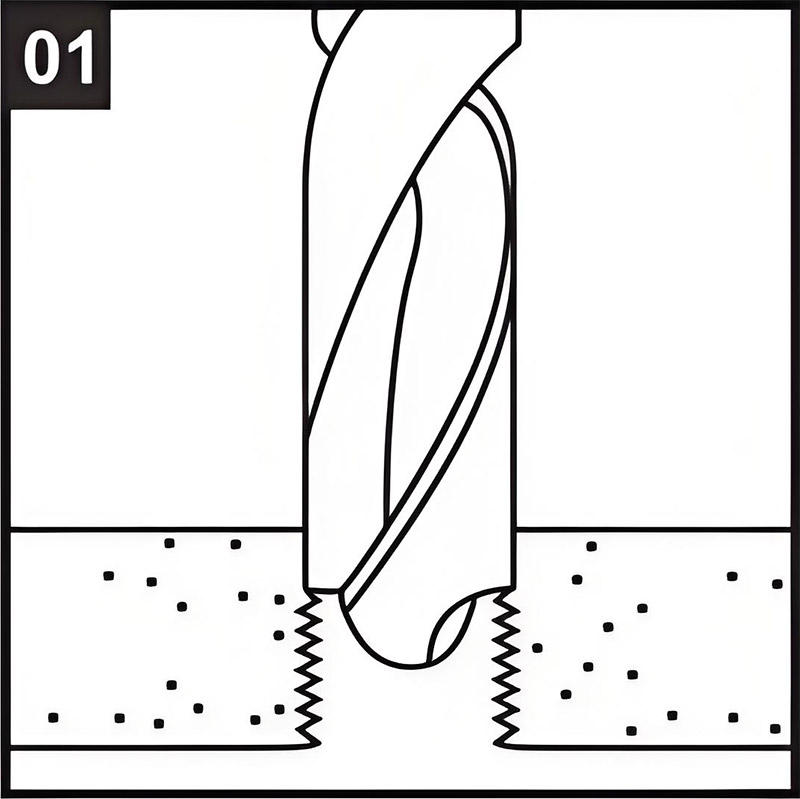
01Drilling:
Drill out a portion of the key-locking insert.
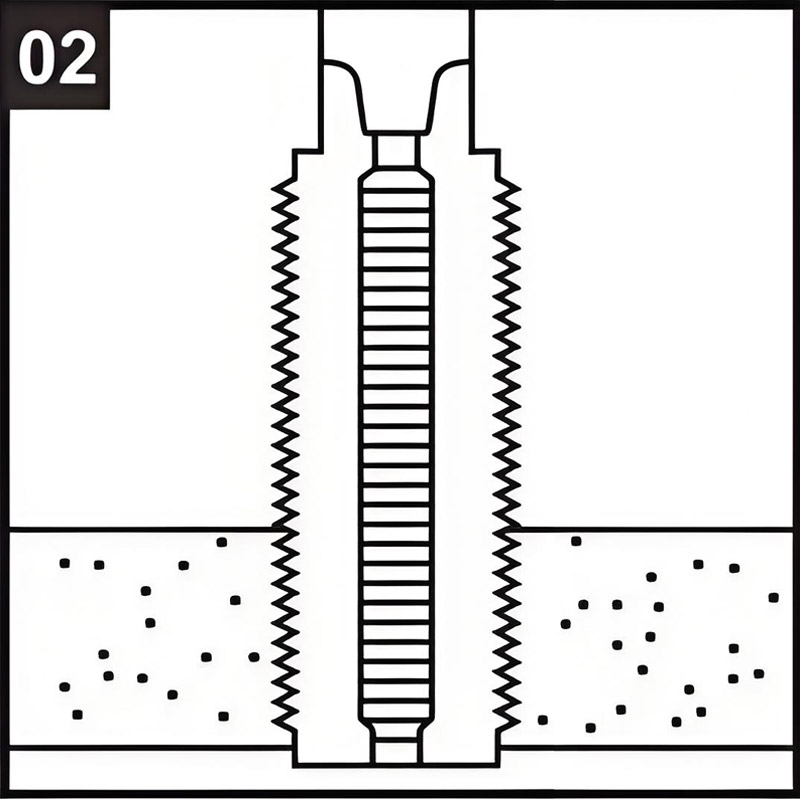
02 Breaking the Keys:
Bend the locking keys inward and break them off.
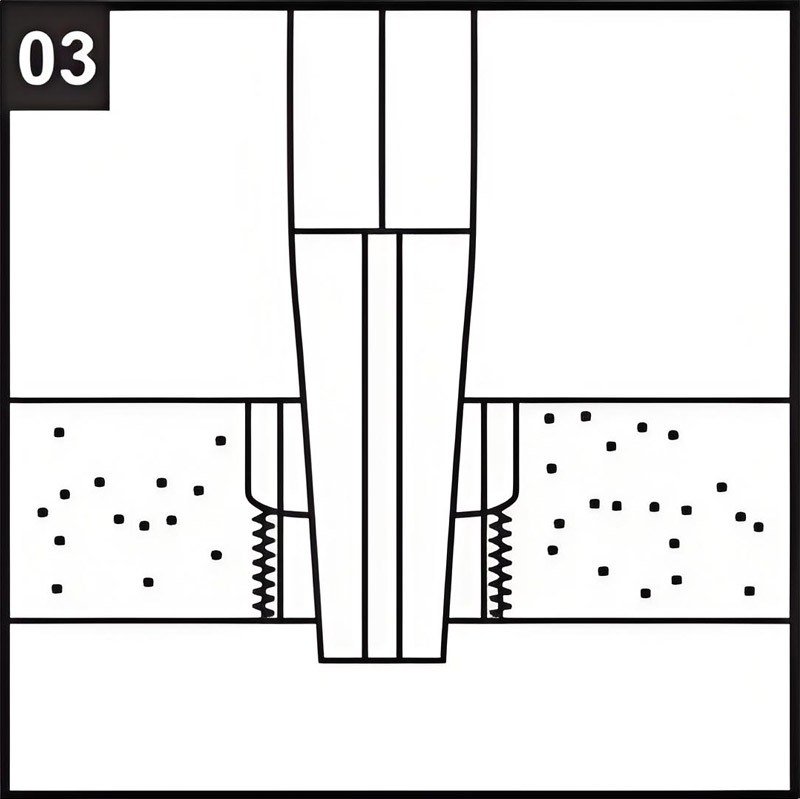
03Removal:
Use an “easy-out tool” or a similar tool to unscrew and remove the insert.
04Reinstallation:
A new key-locking insert can then be installed.
 Product Parameters
Product Parameters Specification Table for Key-locking Insert
| Internal Thread | External Thread | Length | Tap Drill Size | Tapped Hole Thread | Tap Depth |
| Miniature | |||||
| M2×0.4 | M4×0.7 | 3 | 3.4 | M4×0.7 | 4 |
| M2.5×0.45 | M4.5×0.75 | 3.8 | 3.9 | M4.5×0.75 | 5 |
| M3×0.5 | M5×0.8 | 4.2 | 4.4 | M5×0.8 | 5.5 |
| M4×0.7 | M6×0.75 | 5.2 | 5.5 | M6×0.75 | 6.5 |
| Thin-Wall | |||||
| M5×0.8 | M8×1.25 | 8 | 6.9 | M8×1.25 | 9.5 |
| M6×1.0 | M10×1.25 | 10 | 8.8 | M10×1.25 | 11.5 |
| M8×1.25 | M12×1.25 | 12 | 10.8 | M12×1.25 | 13.5 |
| M8×1.0 | M12×1.25 | 12 | 10.8 | M12×1.25 | 13.5 |
| M10×1.5 | M14×1.5 | 14 | 12.8 | M14×1.5 | 15.5 |
| M10×1.25 | M14×1.5 | 14 | 12.8 | M14×1.5 | 15.5 |
| M12×1.75 | M16×1.5 | 16 | 14.75 | M16×1.5 | 17.5 |
| M12×1.25 | M16×1.5 | 16 | 14.75 | M16×1.5 | 17.5 |
| Heavy-Duty | |||||
| M4×0.7 | M8×1.25 | 8 | 6.9 | M8×1.25 | 9.5 |
| M5×0.8 | M10×1.25 | 10 | 8.8 | M10×1.25 | 12.5 |
| M6×1.0 | M12×1.25 | 12 | 10.8 | M12×1.25 | 14.5 |
| M8×1.25 | M14×1.5 | 14 | 12.8 | M14×1.5 | 16.5 |
| M8×1.5 | M14×1.5 | 14 | 12.8 | M14×1.5 | 16.5 |
| M10×1.0 | M16×1.5 | 16 | 14.75 | M16×1.5 | 18.5 |
| M10×1.25 | M16×1.5 | 16 | 14.75 | M16×1.5 | 18.5 |
| M12×1.75 | M18×1.5 | 18 | 16.75 | M18×1.5 | 20.5 |
| M12×1.25 | M18×1.5 | 18 | 16.75 | M18×1.5 | 20.5 |
| M14×2.0 | M20×1.5 | 20 | 18.75 | M20×1.5 | 22.5 |
| M14×1.5 | M20×1.5 | 20 | 18.75 | M20×1.5 | 22.5 |
| M16×2.0 | M22×1.5 | 22 | 20.5 | M22×1.5 | 24.5 |
| M16×1.5 | M22×1.5 | 22 | 20.5 | M22×1.5 | 24.5 |
| M18×1.5 | M24×1.5 | 24 | 22.5 | M24×1.5 | 26.5 |
| M20×2.5 | M30×2.0 | 30 | 28 | M30×2.0 | 34.5 |
| M20×1.5 | M30×2.0 | 30 | 28 | M30×2.0 | 34.5 |
| M22×1.5 | M32×2.0 | 32 | 30 | M32×2.0 | 36.5 |
| M24×3.0 | M33×2.0 | 33 | 31 | M33×2.0 | 37.5 |
| M24×2.0 | M33×2.0 | 33 | 31 | M33×2.0 | 37.5 |
ANSI Key-Locking Thread Insert Specifications
| Internal Thread | External Thread | Length | Tap Drill Size | Tapped Hole Thread | Tap Depth |
| Miniature | |||||
| 2-56 | 8-32 | 0.12 | 0.134 | 8-32 | - |
| 4-40 | 10-32 | 0.17 | 0.161 | 10-32 | - |
| 6-32 | 12-28 | 0.17 | 0.187 | 12-28 | - |
| 8-32 | 1/4-28 | 0.22 | 0.228 | 1/4-28 | - |
| Thin-Wall | |||||
| 10-24 | 5/16-18 | 7.9 | 6.4 | 5/16-18 | 9.4 |
| 10-32 | 5/16-18 | 7.9 | 6.4 | 5/16-18 | 9.4 |
| 1/4-20 | 3/8-16 | 9.4 | 8.5 | 3/8-16 | 10.9 |
| 1/4-28 | 3/8-16 | 9.4 | 8.5 | 3/8-16 | 10.9 |
| 5/16-18 | 7/16-14 | 10.9 | 9.1 | 7/16-14 | 12.4 |
| 5/16-24 | 7/16-14 | 10.9 | 9.1 | 7/16-14 | 12.4 |
| 3/8-16 | 1/2-13 | 12.7 | 11.5 | 1/2-13 | 14.2 |
| 3/8-24 | 1/2-13 | 12.7 | 11.5 | 1/2-13 | 14.2 |
| 7/16-14 | 9/16-12 | 14.2 | 13.1 | 9/16-12 | 15.7 |
| 7/16-20 | 9/16-12 | 14.2 | 13.1 | 9/16-12 | 15.7 |
| 1/2-13 | 5/8-11 | 15.7 | 14.7 | 5/8-11 | 17.2 |
| 1/2-20 | 5/8-11 | 15.7 | 14.7 | 5/8-11 | 17.2 |
| Heavy-Duty | |||||
| 8-32 | 5/16-18 | 7.9 | 6.4 | 5/16-18 | 9.4 |
| 10-24 | 3/8-16 | 7.9 | 6.4 | 3/8-16 | 9.4 |
| 10-32 | 3/8-16 | 7.9 | 6.4 | 3/8-16 | 9.4 |
| 1/4-20 | 7/16-14 | 9.4 | 9.1 | 7/16-14 | 10.9 |
| 1/4-28 | 7/16-14 | 9.4 | 9.1 | 7/16-14 | 10.9 |
| 5/16-18 | 1/2-13 | 10.9 | 11.5 | 1/2-13 | 12.4 |
| 5/16-24 | 1/2-13 | 10.9 | 11.5 | 1/2-13 | 12.4 |
| 3/8-16 | 9/16-12 | 12.7 | 13.1 | 9/16-12 | 14.2 |
| 3/8-24 | 9/16-12 | 12.7 | 13.1 | 9/16-12 | 14.2 |
| 7/16-14 | 5/8-11 | 15.7 | 14.7 | 5/8-11 | 17.2 |
| 7/16-20 | 5/8-11 | 15.7 | 14.7 | 5/8-11 | 17.2 |
| 1/2-13 | 3/4-16 | 15.7 | 17.8 | 3/4-16 | 17.2 |
| 1/2-20 | 3/4-16 | 15.7 | 17.8 | 3/4-16 | 17.2 |
| 9/16-12 | 3/4-16 | 20.6 | 17.8 | 3/4-16 | 22.1 |
| 9/16-18 | 3/4-16 | 20.6 | 17.8 | 3/4-16 | 22.1 |
| 5/8-11 | 7/8-14 | 22.0 | 21.0 | 7/8-14 | 23.5 |
| 5/8-18 | 7/8-14 | 22.0 | 21.0 | 7/8-14 | 23.5 |
Thread Insert Production Process
Crafted with Skill·Made with Dedication — The Art of Precision Thread Insert Manufacturing
Please feel free to email us:arvin540@foxmail.com
 Recommended Applications
Recommended Applications Key-locking thread inserts Today,they are widely used in aerospace, aviation, instrumentation, rail transit, hydraulic and electric equipment, chemical fiber machinery, textiles, and other applications requiring high thread strength.
 Related Recommendations
Related Recommendations
Top

Follow us